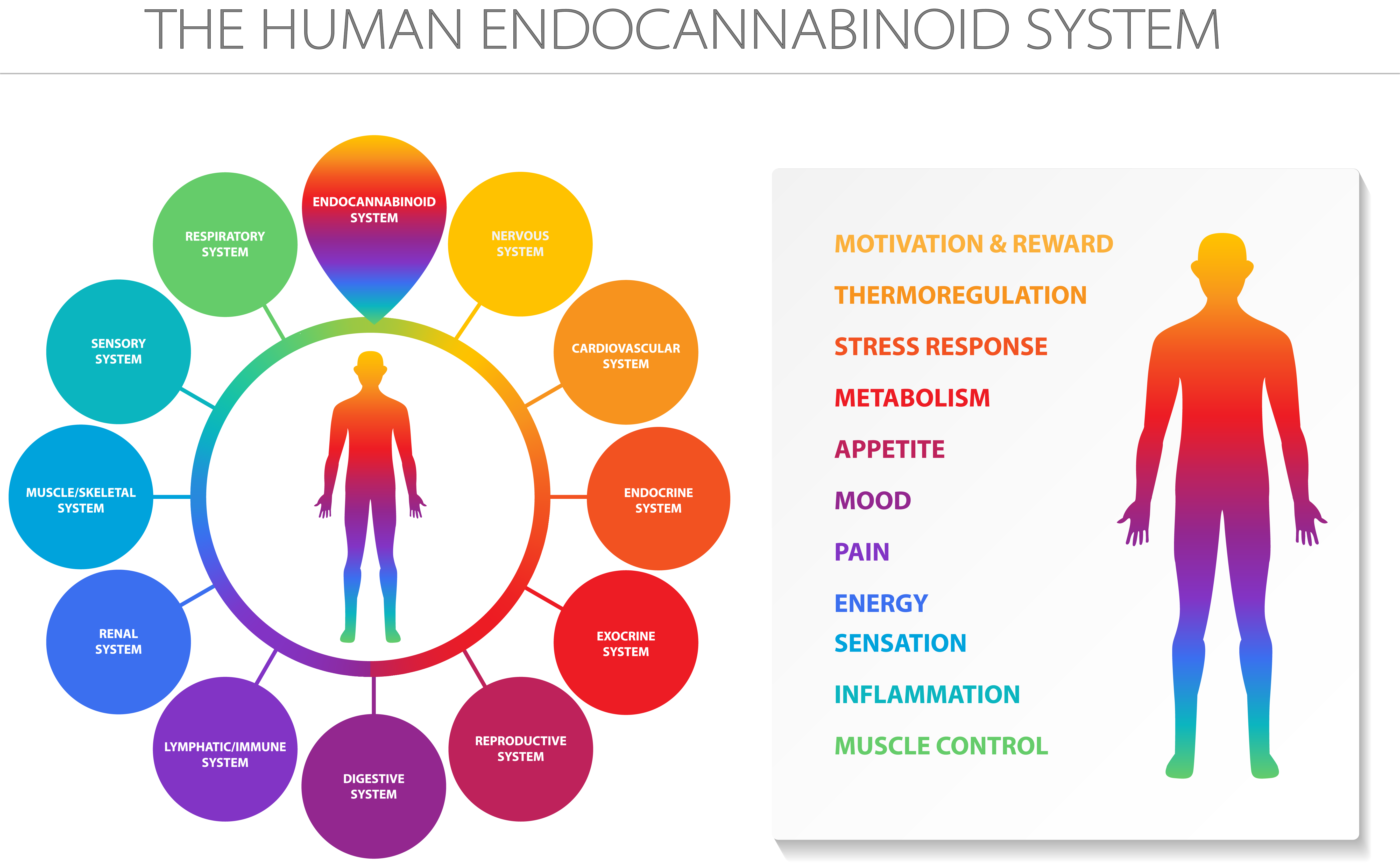
What Is The Endocannabinoid System?
Cannabis has been at the forefront of one of contemporary science’s most thrilling and exciting advances. Work on the impact of marijuana contributed directly to the detection of a previously unexplained biochemical signaling mechanism in the human body, the Endocannabinoid System. This system plays a key role in controlling our metabolism, attitude, and daily life.
Named after the weed plant “Cannabis Sativa” and its active component delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the Endocannabinoid System (EC) is a complex signaling network within the brain and body. This system controls physiological and multiple important functions, such as:
- How does the individual think?
- How does the person move around the environment?
- How quick are the individual’s reflexes?
- How does the host respond to certain situations?
- How does the person feel?
Our body constantly produces natural chemicals to help the body stay functional and to control our daily chores, movements, interactions, etc. The natural chemicals that interact within our individual EC systems are known as cannabinoids. Like THC, these chemicals interact with the EC system to help us regulate the body functions with ease.
How Does CBD Interact with the Endocannabinoid System?
As we all know, CBD (Cannabidiol) is quite famous for its anti-inflammatory properties. Recently, it became even more popular when manufacturers started creating creams, lotions, and other products with CBD to offer non-high and non-intoxicating anti-inflammatory attributes of the hemp plant.
CBD, the common cannabis plant compound, has become a hot topic in recent studies for its anti-inflammatory properties and potential to help relieve anxiety in humans and other mammals. However, CBD also interacts with our EC system.
CBD helps combat with CECD (Clinical Endocannabinoid Deficiency Syndrome), a condition in which a body does not produce enough natural chemicals. This alteration and lack of natural CBD in the system may lead to Fibromyalgia, Parkinson’s, and Schizophrenia, among other diseases.
CBD boosts the natural functioning of the EC system to help regulate the host’s physiological functions even when the body lacks natural chemicals and CBD.
Moreover, researchers have also seen positive results for CBD and the EC system to help eliminate substance abuse and other self-destructive tendencies among humans. CBD helps keep everything in place and keeps the EC system working efficiently.
How Does THC Interact with the Endocannabinoid System?
THC, often considered the counterpart to CBD, negatively impacts the EC system. Researchers have shown THC overwhelms the EC system. Moreover, THC easily binds with cannabinoid receptors all over the brain and body. This binding interferes with the capacity of natural cannabinoids to do their job of controlling the neuron-to-neuron coordination.
When the body loses its fine-tuning, THC can throw off balance the entire network, and the EC system starts working irregularly. Since cannabinoid receptors are found in many parts of the brain and body, THC’s effects are broad.
It may delay a person’s response time, which can hinder driving or other motor-skill abilities. THC may also impede the ability to recall events that have just happened, trigger fear and paranoia, and influence judgment.
THC often stimulates regions of the brain that make an individual feel healthy and good about themselves. This may imitate the sensation of being “high.” However, over time, THC will alter how the EC system functions in these brain areas, which may contribute to perception, depression, and mental health issues.
What Is the Bottom Line?
CBD helps the EC system working normally and in an efficient manner. On the other hand, THC alters the working of the EC system and may result in several mental health problems. CBD boosts the cognitive processes and other physiological functions, whereas THC impairs judgment and hinders the host’s motor skills.